MIDDLE EAST TAX ALERT | UAE | Timely insights into the Ministerial decisions released on the UAE Electronic Invoicing System (EIS)
The UAE Ministry of Finance (MoF) has issued Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025 on the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS) and Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025 on its implementation aimed at enhancing transparency, improving compliance, and aligning the UAE with global best practices in tax digitalisation.
These two Ministerial decisions follow the recent UAE VAT executive regulations amendments to align with the upcoming e-Invoicing compliance and aim at clarifying:
- Scope of the e-Invoicing implementation in terms of the revenue threshold
- Taxpayers caught in different implementation waves and the related timelines
- The much-awaited provisions related to transactions that are now officially excluded from e-Invoicing obligations
While these decisions have given a relief for taxpayers engaged in financial services and certain international transportation services, it has also cast a wider net by enforcing a low revenue threshold of AED 50 million for the first wave of taxpayers for which mandatory e-Invoicing compliance applies.
It is important to note that the first wave of taxpayers, except those participating in the pilot program, will go-live on the January 1, 2027.
Key Highlights:
- Establishment of the Electronic Invoicing System (Decision No. 243/2025)
- Mandatory Scope:
- Applies to all businesses conducting business activities in the UAE, unless specifically excluded.
- Applies to all businesses conducting business activities in the UAE, unless specifically excluded.
- Key Exclusions:
- Government entities performing sovereign activities according to the UAE VAT laws.
- International airline passenger transportation and ancillary services where electronic ticket is issued to passengers, mostly Business to Consumer (B2C) use cases.
- Certain international transportation of goods, i.e. cargo services where airway bills are issued.
- Exempt or zero-rated financial services (as per Article 42 of the VAT Executive Regulation).
- Other categories as determined by the Minister.
- Obligations on Businesses:
- E-Invoices and Credit Notes must be issued and transmitted through the EIS within 14 days of the transaction. The “date of business transaction” has been defined in the ministerial decision to mean earlier of the date on which the business transaction occurred or the date of receipt of payment. This leaves room for further clarification especially around requirements for continuous supplies following specific date of supply rules under the UAE VAT laws.
- Both issuers and recipients are required to appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) to manage the exchange and reporting of e-Invoices.
- Additional Provisions:
- Agents and self-billing arrangements are specifically recognized in these decisions.
- Voluntary compliance is permitted, but once opted in, all EIS obligations apply.
- Reporting requirements to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) will be strictly enforced.
- Phased Implementation Timeline (Decision No. 244/2025)
The rollout of mandatory e-invoicing will take place in phases, based on revenue thresholds and taxpayer type:
| Category | Appointment of Service Provider | Mandatory Implementation |
| Large Businesses (Revenue ≥ AED 50M) | By July 31, 2026 | From January 1, 2027 |
| Other Businesses (Revenue < AED 50M) | By March 31, 2027 | From July 1, 2027 |
| Government Entities | By March 31, 2027 | From October 1, 2027 |
- Pilot Programme: Launches July 1, 2026, allowing selected taxpayers (to be notified by the Ministry as being included in the taxpayer working group) to test the system under FTA and Ministry oversight.
- Voluntary Adoption: Open to all businesses from July 1, 2026.
- B2C Transactions: Currently excluded from the mandatory regime until a later date to be specified by the Minister.
Key Takeaways for Businesses:
- Start Early: Assess your systems readiness, Order to Cash (O2C), Purchase to Pay (P2P), wider finance and billing processes, system dataflows, and invoicing workflows. Understand how your overall operations are going to be impacted by e-Invoicing and e-Reporting.
- Plan for Compliance: Identify when your business falls into the mandatory implementation phases. This is particularly crucial for large taxpayers with businesses in different verticals enjoying special VAT treatments (such as financial services or international transportation).
- Select Accredited Service Provider: Understand your requirements and assess the ASPs, based on the official Ministry’s list, to ensure the best fit for your organisation.
- Change Management: All key stakeholders in finance, tax and IT teams need to be aware on structured e-Invoicing and reporting obligations and how their processes are likely to change.
Final Thoughts:
The introduction of the UAE Electronic Invoicing System is a transformative change in the country’s regulatory landscape. Businesses should act now to evaluate their processes, engage with service providers, and prepare for the phased rollout beginning in July 2026.
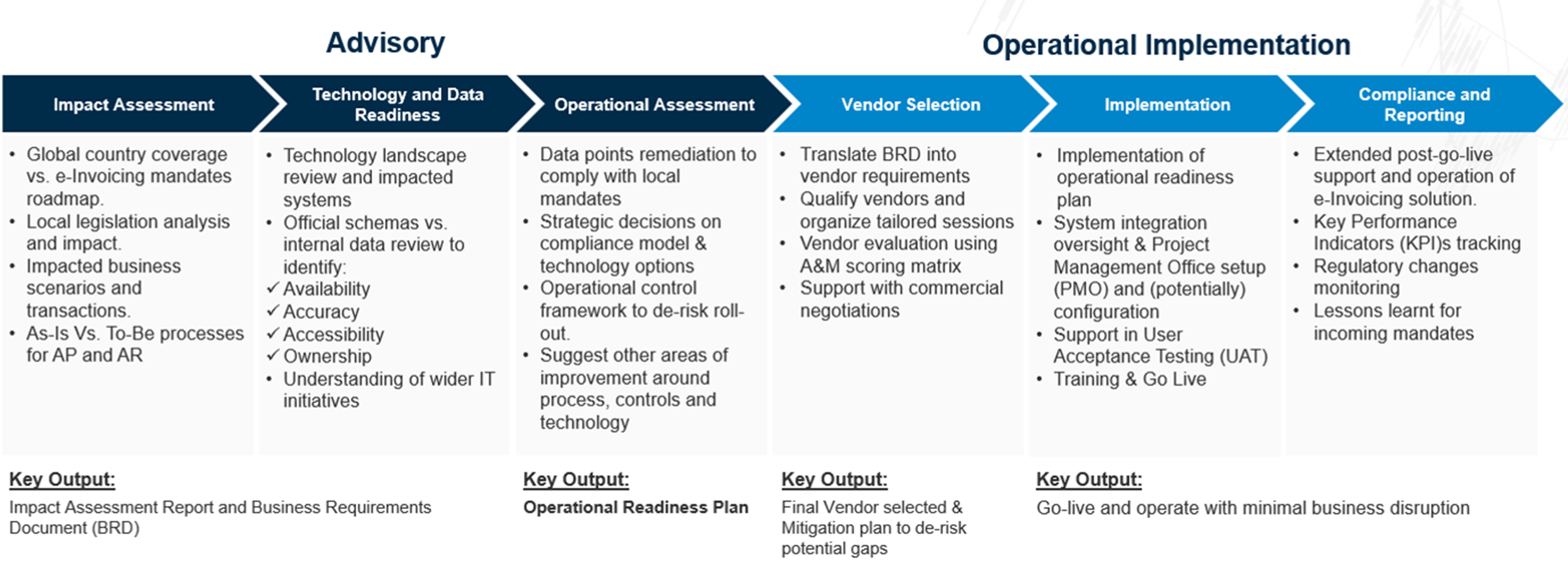
At A&M, we have developed a standard comprehensive approach for operational e-Invoicing readiness:
Get in touch with one of our experts today.




