Mixed Q3 2022 Financial Results, Continued Production Issues and an Improving Microchip Outlook Result in an Unclear Path Ahead Moving into 2023
Inflation saw marginal improvement month-over-month, decreasing from 8.2 percent in September to 7.7 percent in October. Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and suppliers continue to battle production issues, supply chain disruptions and an elevated raw material pricing environment. Automotive sales and inventories both improved in October, as the semiconductor industry is beginning to see signs of stabilization.
In this issue, A&M analyzes the changing nature of noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) in electric vehicles (EVs) as the selected topic for the November Industry Focus.
In transaction news, OEMs continue to partner with technology firms to advance software and entertainment features in their vehicles. Additionally, Renault plans to split into five separate businesses, including the formation of a joint venture and spinning off of its EV unit.
In regulatory news, the U.S. government is moving towards a deadline for providing automakers with further clarifications on EV tax credits, receiving concerns from both domestic and foreign automakers. Also, the European Union (EU) has approved an agreement to effectuate a sale ban on internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles by 2035.
Additional November insights are included below.
Financial Performance
Auto Forecast Solutions’ (AFS) latest numbers show that part shortages, shutdowns and delays have resulted in approximately 3.9 million lost vehicles globally during calendar year 2022, ultimately leading to the recovery of 30,000 cars week-over-week. Although several OEMs are continuing to struggle with manufacturing issues, automotive chip production capacity has begun to stabilize, which could ease the supply crunch and shorten production bottlenecks. Furthermore, China may lessen the severity of its COVID restrictions, potentially reducing the number of additional vehicle losses and increasing the supply of semiconductors. The latest AFS estimates suggest an improved industry outlook, as approximately 4.3 million total cars and trucks will be affected by chip-related disruptions in 2022, an improvement of nearly 100,000 vehicles from the prior month.
EV supply chains are changing, as OEMs are under pressure and face the challenge of developing a complex and regionalized supplier network to help produce EVs, while maintaining EV tax credit eligibility. With these difficult circumstances, OEMs and suppliers are pushing to extremes to satisfy demand for both the crucial materials for EVs and EVs themselves. This has resulted in the industry looking to boost mining in the U.S. and exploring the ocean floor. In order to meet the net zero carbon emissions goal, the auto industry alone would require approximately 127 additional mines for lithium, nickel and cobalt to reach EV demand projections in 2030. Automakers have already begun teaming up with mining companies but will require a greater supply of EV materials to successfully transition to an electric future.
Industry Update
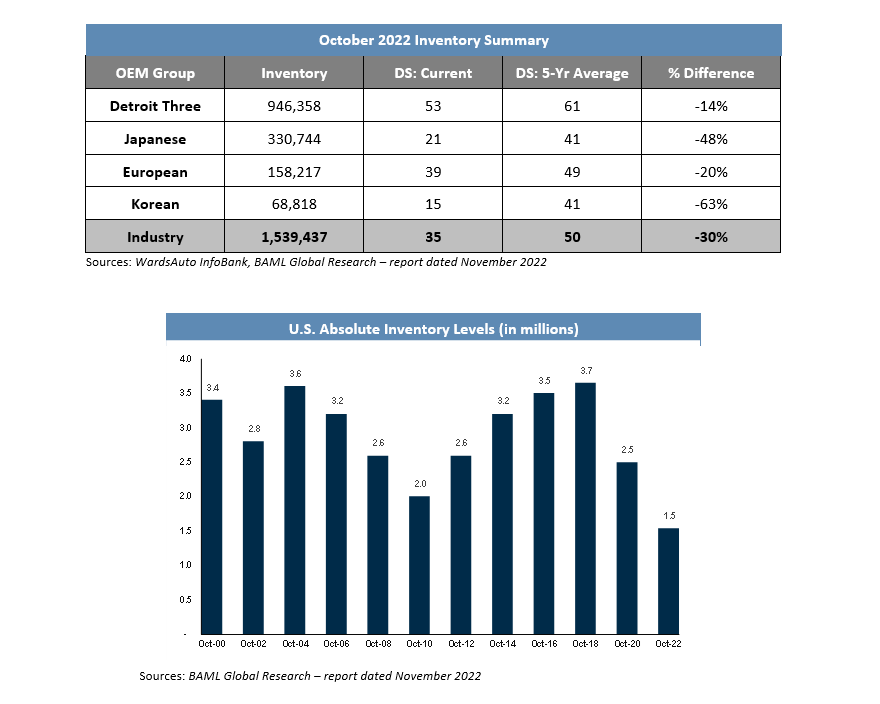
Automotive inventory increased by 111,000 units in October, resulting in approximately 1.54 million total units. This translates to a days’ supply (DS) that is 30 percent below the five-year average at 35 DS. Despite being well below the industry’s inventory standard, the increase marks the second consecutive month of inventory build and records the highest vehicle level since April 2021. The continuous rise of interest rates coupled with persistent inflationary conditions and ongoing recessionary fears may result in lasting reductions in consumer demand for automobiles, ultimately limiting sales and boosting inventory levels.
New light vehicle sales in the U.S. increased 12.5 percent year-over-year in October with a 14.9 million seasonally adjusted annualized rate (SAAR) of sales, while the full-year sales pace is tracking at 13.7 million units. Supply chain complications, in addition to ongoing macro-level challenges, may extend unresolved production issues for auto and parts makers in the near-term through 2022 and into 2023. Although sales typically function as a product of inventory, this could create a restraint on production levels and subsequently hinder sales performance while gradually growing inventory on dealer lots. Average transaction prices also increased year-over-year in October, resulting in a 2.9 percent increase to $44,625 per vehicle.
Industry Focus – Changing Nature of NVH in EVs
As the development of EVs accelerates, OEMs and suppliers are beginning to focus on developing solutions to another obstacle in EV adoption. In previous industry focus sections, A&M has analyzed several different hurdles that OEMs and suppliers are facing in their transition to EVs, including battery materials, customer acceptance issues and the power grid. Now, the automotive industry is being challenged to resolve a key issue: adapting to the changes of noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) in a new age of EVs.
In this month’s industry focus section, A&M explores the evolution of NVH in electric vehicles, the growing demand for NVH testing and several different strategic partnerships that will increase OEMs’ and suppliers’ competitive positioning within the EV market.
Noise, Vibration & Harshness: History, ICE and EVs
Noise, Vibration and Harshness is an important part of an automobile’s makeup. It measures several different aural and tactile vehicle characteristics based on operational experiences. Noise and vibration can be readily assessed, while harshness is more subjective and is evaluated by human perception to noise frequencies and vehicle structure. NVH is impacted by an automobile’s interior and exterior design, in addition to its mechanical and electrical systems. NVH is undergoing significant developments to adjust to EVs; the NVH materials market was valued at $10.59 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow to $11.35 billion and $15.10 billion by 2022 and 2026, respectively, as stated by Globe Newswire.
Historically, ICE vehicles would mask the tire and aerodynamic noises consumers would hear in their cars. Recent studies have shown EVs produce louder interior noises and stronger vibrations while driving, since EVs don’t have the noise dampening effects of louder ICEs and are unable to absorb vibrations as well as ICE vehicles on surface areas due to their differing mechanical structure. EVs suffer from sub-optimal noise levels caused by tire, road and wind sounds, as well as whine emanated from a car’s electric motor and other essential component parts. In order to prevent a perception by consumers that EVs are less pleasant to ride in than ICE vehicles, OEMs and suppliers will have to optimize these vehicle performance characteristics to emit low noise and vibration, while providing a comfortable and quiet ride.
EVs currently being produced are becoming lighter, due to fewer parts and material changes, which is creating more apparent noise issues when it comes to NVH. Automotive manufacturers are investigating different ways to dampen noise, such as changing the type of dampening material to minimize additional mass and cost, specific placement of noise dampening materials within a car, and different surface dampening techniques. As OEMs continue to innovate with EV design, it will be important to adapt to the changing consumer trends of softer, quieter rides. Auto suppliers have already modified their respective technologies and processes to focus on the advancement of NVH performance. Some suppliers have been able to alter their steering, driveline, and other value-creating technologies to increase vehicle range, safety and environmental benefits, while also minimizing interior noise and reducing production costs.
Strategic Partnerships in NVH Testing
Auto and part manufacturers have been heavily investing in NVH testing because of its critical nature in developing automobiles, especially EVs. NVH testing allows auto manufacturers to stress test an electric vehicle under different conditions while utilizing electric sensors and monitors through various simulation technologies. It has become so vital that different companies have begun assisting OEMs with NVH testing even before integrating components into the vehicle to keep up with industry regulations and market demand.
In recent years, automotive supplier Siemens has been able to leverage its innovative engineering and software testing solutions platform, Simcenter, to develop strategic global partnerships and position itself for an electric future. Siemens has partnered with SsangYong Motor Company, the fourth largest South Korean-based automotive manufacturer, Karma Automotive, a U.S.-based electric automaker, and heavy-duty truck manufacturer SAIC HONGYAN Automotive. In all strategic collaborations listed, the OEMs were able to enhance their simulation and testing processes, develop more efficient production methods, realize significant cost savings and meet new regulatory standards.
Superb NVH ratings were already a key differentiator among mass and luxury ICE vehicles. With EVs, NVH will not only continue to be a main factor in distinguishing vehicles but may also be critical for the overall adoption of EVs by consumers.
Transaction Activity
In recent transaction news, Renault continues the OEM trend of partnerships with technology companies as the auto manufacturer announced its plans to expand its collaboration with Google to enhance software capabilities in vehicles. The French-based OEM also disclosed its intent to separate into five businesses, including a spin-off of its EV unit and the joint venture analyzed below. Additionally, Stellantis and Foxconn have teamed up to create a new joint venture, Mobile Drive, focused on infotainment systems, telematics and cloud-based technologies.
See below for additional detail on recently announced transactions.

- Cummins and Tata Motors, India’s leading auto manufacturer, have signed an agreement for the companies to collaborate on designing and developing hydrogen-powered internal combustion engines, fuel cells and battery electric vehicle systems. The partnership will accelerate sustainable growth and assist in moving towards India’s net zero emissions target by 2070.
- Renault and China-based auto manufacturer, Geely recently struck a deal to form an equally held joint venture that intends to supply gas powered engines and hybrid technologies. The joint venture will supply ICEs and the respective technology to their own brands as well as to other OEMs. Renault and Geely also have an existing joint venture in South Korea.
- Nikola Motors and U.S.-based EV infrastructure and charging operator, ChargePoint, have announced their partnership to boost the deployment of a charging infrastructure for commercial EVs. With access to ChargePoint’s products, the deal will reduce the time required for infrastructure projects and allows Nikola to leverage an EV charging network to better manage its plan schedules and streamline deliveries.
- Lidar suppliers Velodyne and Ouster have reached a merger deal expected to close in the first half of 2023, with each constituent owing 50 percent of the combined company. Velodyne and Ouster manufacture precision lidar sensors that support self-driving vehicles. Through the merger, the companies will be able to create operational synergies and save $75 million across engineering and manufacturing related expenses.
Regulatory Landscape
U.S. EV Tax Credits: Under the recently signed Inflation Reduction Act, the U.S. Treasury is mandated to provide automakers with further guidance in clarifying the parameters for EV tax credit eligibility by December 31. Several U.S.-based OEMs have urged the U.S. government to maximize flexibility, as auto manufacturers must localize their EV supply chains and reduce exposure to foreign-based materials and production. Additionally, several allied nations of the U.S., including Japan, South Korea, the European Union (EU) and Brazil, have expressed concerns over the legislation stating that it risks economic damages and puts foreign OEMs at a disadvantage.
Ford Litigation: In relation to a lawsuit that started in 2015, Ford Motor Co. has been ordered by a federal jury in Detroit to pay Versata Software $104.6 million. The payment is due to Ford breaching its licensing contract and misappropriating trade secrets dating back to the early 2000’s. Versata claims that Ford began copying its software, which resulted in $59.9 million of damages for the software company.
EU ICE Ban: The EU has reached a political agreement to effectively ban the sale of ICE vehicles beginning in 2035. Under the planned legislation, emissions from new automobiles must be 55 percent and 50 percent lower than 2021 levels for cars and vans, respectively. The sale ban on gas-powered vehicles is part of the EU’s broader plan, which is targeting net zero emissions by 2050
Porsche Lawsuit: In a class-action lawsuit, a final order was approved for an $80 million settlement regarding skewed emissions and fuel economy data from Volkswagen Group (VW) and its Porsche unit. The settlement affects vehicles from 2005 to 2020, as the OEM is being accused of physically altering test vehicles affecting emissions results. The court also approved nearly $25 million in legal fees.
Bosch Settlement: In connection with the diesel emissions probes at VW and Stellantis, Bosch has agreed to pay $25 million to settle these claims in California. The German auto supplier allegedly provided hardware, software, and software programming services to VW and Stellantis while evading emissions regulations.
Stay connected to industry financial indicators and check back in December for the latest Auto Industry Spotlight.
Automotive Industry Spotlight Archive



