A look into key focus areas heading into 2025 and a new presidential administration
This edition of the Automotive Industry Spotlight will focus on key industry developments to watch following Donald Trump’s win of the 2024 presidential election.
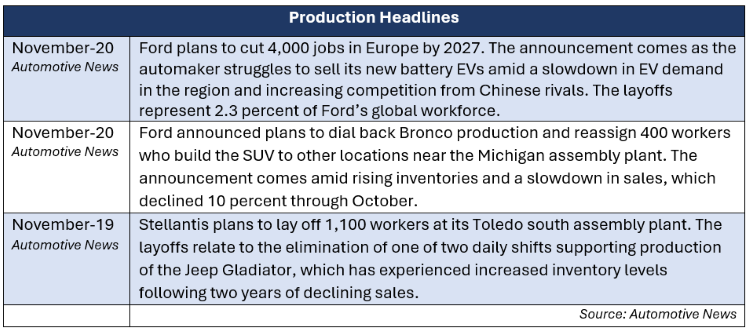
In industry news, Ford announced 4,000 jobs will be cut in Europe as the automaker faces a slowdown in electric vehicle (EV) demand in the region. Rivian formally announced a $5.8 billion joint venture with Volkswagen, aiming to bring next-generation electrical architecture and software to both automakers’ EVs. Volkswagen Group of North America also announced its new CEO, Kjell Gruner, who previously served in executive roles at Porche and Rivian.
In regulatory news, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) fined Ford $165 million related to a failure to meet key recall standards. GM announced a recall of over 500,000 diesel engine vehicles in the U.S. and Canada due to reports of a faulty transmission control valve. Tesla announced its sixth recall of Cybertrucks in the U.S. this year, citing defective drive inverters that were manufactured between late-2023 and mid-2024.
Industry Focus: Post-Election Outlook
With the Trump administration securing a second term in the 2024 U.S. presidential election, the automotive industry is preparing for potential shifts across the industry, spanning from global supply chains to the trajectory of EV adoption. The president elect’s known priorities — which favor domestic manufacturing, reduced regulatory burdens and the promotion of traditional energy sectors — could change the current course that was set under the Biden administration.
Trade Policy: Tariffs and Supply Chains
One of the most immediate areas of focus is trade policy. Trump’s first term was marked by aggressive tariff measures aimed at promoting American industry, and his return to office could bring more of the same. It is worthy to note that the Biden administration kept many of the Trump administration’s tariffs in place and even expanded tariffs in some cases. Trump has indicated that his administration will consider 10 percent to 20 percent tariffs on all imports and has specifically discussed higher tariffs on imports from China and Mexico.1 Higher tariffs on imported vehicles and parts could significantly raise costs for automakers reliant on global supply chains. While some companies may pass these costs onto consumers, others could use this as an impetus to ramp up domestic production. However, these shifts could bring growing pains, especially for manufacturers that have invested heavily in overseas operations. By way of example, Tesla CEO Elon Musk stated that plans for Tesla’s $10 billion gigafactory in Mexico were on pause until the election was decided and next steps were clear.2
A renewed push to renegotiate trade agreements, such as the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), might further encourage reshoring, creating more localized supply chains in North America. The USMCA is scheduled for its first review among the U.S., Canada and Mexico in 2026, which will require trade representatives to come to an agreement on any change in terms. Additionally, trade representatives will either agree to extend the agreement for 16 years or launch annual reviews each year through 2036, which is leading automakers to plead for continuity ahead of the review.3 Furthermore, the Chinese EV automaker BYD is contemplating building a production facility in Mexico. BYD, which produces low-cost EVs, has previously been identified as a potential threat to the competition for EV market share in North America.4 Consideration of BYD’s plant in Mexico will likely play a role in shaping the USMCA negotiations.
Shifts in Regulatory Environment
As the industry adapts to changes in trade policy, it will also likely contend with a vastly different regulatory environment. Trump has historically advocated for deregulation, particularly in sectors like automotive manufacturing, where stringent fuel efficiency and emissions standards have been a challenge for companies. Biden-era federal regulations surrounding fuel efficiency and other emission standards would require automakers to shift nearly 35 percent of production to EVs by 2032 to comply with the standards.5 The incoming Trump administration plans to target these requirements and weaken standards on fuel efficiency and tailpipe emissions. Reduced fuel efficiency standards could mean a reprieve from the steep costs associated with transforming production to meet compliance. It might also allow manufacturers to extend the sales outlook for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles without incurring additional penalties. Further, the possibility of relaxed fuel efficiency standards could provide automakers more time to roll out EV fleets and tackle profitability issues. In fact, time may be exactly what automakers need when it comes to addressing EV profitability concerns. A recent Goldman Sachs research report indicated that EV battery prices could fall nearly 50 percent by 2026, potentially bringing EV costs for consumers on par with ICE vehicle costs.6 The potential deregulation, however, isn’t without its complications. States like California, which maintain their own strict environmental standards, may continue to clash with federal policies, creating a fragmented regulatory landscape.
Electric Vehicles: Tug of War Continues
Perhaps the most pivotal area of change lies in the EV sector. Under the Biden administration, the U.S. made significant strides in laying the groundwork for incentivizing EV adoption, from consumer tax credits to investments in charging infrastructure. Trump’s return to office could signal a reversal of these policies. Federal subsidies for EVs, introduced under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), may be reduced or eliminated altogether, which could slow the progress in EV adoption seen in recent years. Specifically, the Trump administration is expected to remove the $7,500 consumer tax credit for EV purchases.7 Without these incentives, consumers may be less inclined to transition to EVs, and automakers that have invested billions in electrification may find themselves reevaluating their short- and near-term strategies. According to a study by Rystad Energy, tax credits and government subsidies have bolstered EV demand, and countries that removed these incentives have experienced significant declines in EV sales.8 In the U.S., EV incentives and discounts increased in Q3 2024, boosting EV sales compared to Q1 and Q2 as illustrated below.
Trump’s administration is also likely to emphasize traditional energy sources, potentially rolling back federal support for renewable energy and EV infrastructure. However, this doesn’t mean a complete abandonment of the EV sector. Trump’s close ties to Tesla CEO Elon Musk could potentially result in better-than-expected support for the broader EV market, including national charging infrastructure.
For the automotive industry, Trump’s second term represents both an opportunity and a challenge. On one hand, a friendlier regulatory environment and policies favoring domestic production could reduce costs and create jobs, particularly in traditional manufacturing hubs. On the other hand, a potential slowdown in the EV transition and increased geopolitical tensions from trade policies could complicate long-term strategies.
Sources
- The Wall Street Journal: Auto Industry Braces for Whiplash as Trump Takes Power (https://www.wsj.com/business/autos/trump-auto-business-car-sales-126eb40c?mod=autos_more_article_pos1)
- Business Insider: Trump's tariffs will make it hard for automakers — including Tesla — to set up shop in Mexico (https://www.businessinsider.com/trump-tariffs-threaten-elon-musk-tesla-mexico-factory-limbo-2024-11)
- Automotive News: Auto industry preps for unprecedented USMCA review as crucial elections loom (https://www.autonews.com/manufacturing/auto-industry-urges-continuity-ahead-2026-usmca-review/)
- PBS: Small, well-built Chinese electric vehicle poses a big threat to the U.S. auto industry (https://www.pbs.org/newshour/economy/small-well-built-chinese-electric-vehicle-poses-a-big-threat-to-the-u-s-auto-industry)
- Automotive News: Trump administration plans to roll back Biden’s stricter fuel-efficiency standards (https://www.autonews.com/regulation-safety/an-trump-biden-fuel-economy-rollback/)
- Goldman Sachs: Electric vehicle battery prices are expected to fall almost 50% by 2026 (https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/articles/electric-vehicle-battery-prices-are-expected-to-fall-almost-50-percent-by-2025)
- Reuters: Trump’s transition team aims to kill Biden EV tax credit (https://www.reuters.com/business/autos-transportation/trumps-transition-team-aims-kill-biden-ev-tax-credit-2024-11-14/)
- Rystad Energy: EV sales collapse as subsidies and tax credits come to an abrupt halt (https://www.rystadenergy.com/news/ev-sales-collapse-as-subsidies-and-tax-credits-come-to-an-abrupt-halt)
Additional November insights are included below.

Industry Update
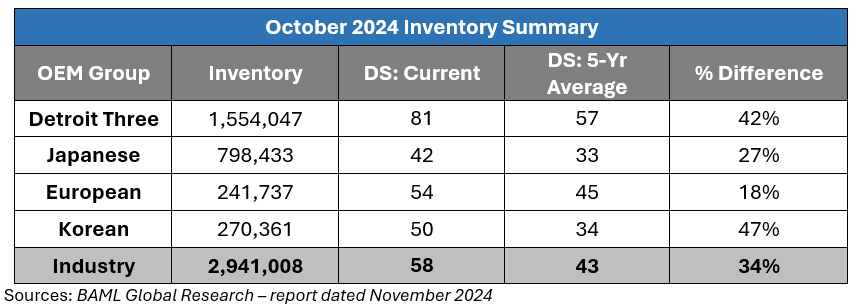
October inventory levels ended at 2.941 million units, a 120,000-unit increase from September. Days’ supply closed at 58, approximately 34 percent above the five-year average. GM (plus 351,000 units) and Ford (plus 24,000 units), led the way for domestic increases while Stellantis saw a 44,000-unit decrease.
Regulatory Landscape
NHTSA fines Ford $165 million: Ford agreed to pay a fine of up to $165 million after failing to recall vehicles with defective rearview cameras in a timely matter and provide accurate and complete recall information. The penalty represents the second-largest civil fine ever levied by the NHSTA.1
GM Recall: GM announced the recall of over 461,000 diesel engine vehicles in the U.S. due to a faulty transmission control valve. Approximately 52,000 additional vehicles in Canada are also impacted by the defect. The recall comes after 11 reported incidents, which included instances of vehicles veering off the road. The recall affects certain production years and models of the Silverado, Sierra, Escalade, Suburban, Tahoe and Yukon that are equipped with the diesel engine.2
Cybertruck Recall: In its sixth recall of the Cybertruck this year, Tesla announced the recall of an additional 2,400 Cybertrucks in the U.S. The recalled electric pickups could experience a loss of drive power, which would increase the risk of a crash. The root of the defect is said to be a faulty drive inverter that was manufactured between November 6, 2023, and July 30, 2024. The recall comes after Tesla announced a recall of more than 27,000 Cybertrucks last month. 3
Regulatory News Source
- Automotive News: NHTSA fines Ford $165 million over delayed backup camera recall (https://www.autonews.com/ford/an-ford-nhtsa-fine-recall-failure/)
- Automotive News: Faulty GM transmission triggers recall of more than 500,000 diesel vehicles in U.S., Canada (https://www.autonews.com/regulation-safety/an-recall-gm-transmission-valve-default/)
- Automotive News: Tesla recalls 2,431 Cybertrucks in sixth U.S. callback this year (https://www.autonews.com/tesla/an-tesla-cybertruck-recall/)
Stay connected to industry financial indicators and check back in December for the latest Auto Industry Spotlight.
Automotive Industry Spotlight Archive




